In situ spectroscopic studies of the one-pot synthesis of composition-controlled Cu–Ni nanowires with enhanced catalytic activity†
Abstract
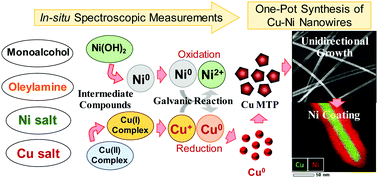
Here, an alcohol reduction method for preparing composition controlled Cu–Ni nanowires (NWs) in high yields is proposed through the selection of an appropriate combination of metallic precursors, alcohol type and surfactant. Also, the mechanism of NW formation was elucidated using morphological, structural and in situ UV-visible and X-ray absorption spectroscopic measurements. In the initial stages of the reaction, the metallic precursors coordinated with amine groups to form complexes. When the temperature of the reactants was increased, Ni formed hydroxide structures such as layered Ni(OH)2, while Cu was partially reduced to Cu+ and coordinated with Cl− ions. At higher temperatures, the Ni2+ ions were reduced to metallic Ni before the formation of metallic Cu. Subsequently, the metallic Ni seeds donated electrons to Cu+ through a galvanic reaction forming Cu seeds. Then, the unidirectional growth progressed due to the etching of the Cu seeds by the chloride ions and the preferential adsorption of the capping agent on the [100] planes of Cu. After the consumption of the Cu ions to form metallic Cu NWs, the Ni ions that remained in the solution were reduced and deposited on the Cu NW surface. The average diameter and length of the Ni-coated Cu NWs were 70 nm and 30 μm, respectively and the composition of Ni varied between 2 and 80 wt%. The catalytic activity of the Cu–Ni NWs was studied through the decoloration reaction of methylene blue, and nanowires with 58 wt% Ni were the most active. These results could be ascribed to the efficient interaction between the Cu core and the Ni sheath.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...