Fluorimetric and colorimetric analysis of total iron ions in blood or tap water using nitrogen-doped carbon dots with tunable fluorescence†
Abstract
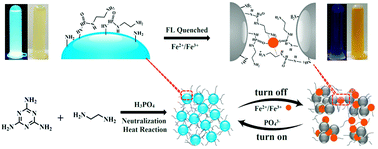
Fluorimetric and colorimetric analysis strategies have been developed for simultaneously probing Fe3+ and Fe2+ ions in blood or tap water using nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-Cdots). Herein, the N-Cdots were prepared using melamine by a neutralization heat reaction one-step synthesis route showing high aqueous solubility and environmental stability. Importantly, unlike common carbon dots (Cdots) that generally display one emission of blue fluorescence, they can display excitation-dependent tunable emissions. Moreover, the bright blue-green fluorescence of N-Cdots could be specifically quenched by Fe3+ or Fe2+ ions simultaneously, showing a color change. Herein, the fluorescent quenching of N-Cdots is thought to result from the aggregation of N-Cdots triggered by the unique coordination interactions between Fe3+ or Fe2+ ions and amine and amide groups of N-Cdots. The developed analysis strategies were employed for the evaluation of the total iron levels in blood or tap water, with a detection limit down to about 5.0 nM, exemplified for Fe3+ ions. These strategies could be promising for use in practical applications for the clinical diagnosis of iron-relative diseases (i.e., anemia and cancers) and environmental monitoring of iron pollution. In addition, this one-step neutralization heat reaction route as a facile green synthesis candidate may be tailored for the fabrication of a variety of Cdots, especially those with doped heteroatoms (i.e., nitrogen) for extensive applications in biomedical and environmental fields.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...