Hemisynthesis, computational and molecular docking studies of novel nitrogen containing steroidal aromatase inhibitors: testolactam and testololactam†
Abstract
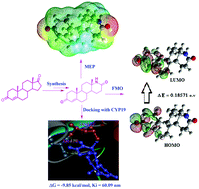
Testololactone (10) and testolactone (11) represent aromatase inhibitors containing lactone rings. We previously reported their hemisynthesis from the most common phytosterols, which are highly abundant in nature. Herein, we report the synthesis of their nitrogen congeners: testololactam (3) and testolactam (8). The reaction process involves the conversion of 4-androstene-3,17-dione to its corresponding oxime using hydroxylamine hydrochloride, whose Beckmann rearrangement under acid conditions yielded the desired testololactam (3). However, testolactam (8) was formed by the Beckmann rearrangement of the oxime (7) of 1,4-androstene-3,17-dienone (6). This expeditious reaction scheme may be exploited for the bulk production of testololactam (3) and testolactam (8). Theoretical DFT studies concerning the structural and electronic properties of all the end products were carried out using the Becke three-parameter Lee–Yang–Parr function (B3LYP) and 6-31G(d,p) level of theory. Molecular electrostatic potential map and frontier orbital analysis were carried out. The HOMO–LUMO energy gap was calculated, which allowed the calculation of relative reactivity descriptors like chemical hardness, chemical inertness, chemical potential, nucleophilicity and electrophilicity index of the synthesized products. The molecular docking studies of testololactam (3), testolactam (8) and testololactone (10), with aromatase (CYP19) revealed binding free energies of (ΔGb) = −9.85, −9.62 and −10.14 kcal mol−1 respectively, compared to the standard testolactone (11), a well-known aromatase inhibitor sold under the brand name TESLAC, which exhibited a binding free energy (ΔGb) of −10.29 kcal mol−1 with an inhibition constant Ki of 28.87 nM. The docking study revealed that the nitrogen congeners exhibit a relatively lower but appreciable therapeutic efficiency to be used as aromatase inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...