Quantum chemical and electrochemical studies of lysine modified carbon paste electrode surfaces for sensing dopamine
Abstract
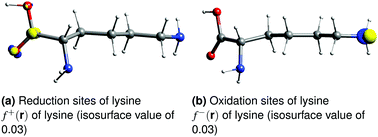
In the current work, we have improved the sensitivity of a carbon paste electrode (CPE) from lysine for the sensitive detection of dopamine (DA). We have used density functional theory based quantum chemical calculations to characterize the lysine modified CPE (LMCPE) surface at the atomic scale. Quantum chemical modeling with analytical Fukui results suggests that lysine acts as an electrocatalyst on the LMCPE surface by increasing its active electron transfer (ET) sites. The obtained voltammetric results are in good agreement with the theoretical observations and electrochemical results showed that the LMCPE surface is stable and efficient in sensing DA in commercial samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...