Electrochemically synthesized faceted CuInTe2 nanorods as an electron source for field emission applications†
Abstract
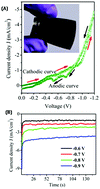
Herein, CuInTe2 (CIT) thin films with faceted nanorod-like morphology have been synthesized on a flexible molybdenum foil using a water-based low-cost electrodeposition technique. The co-deposition potential for CIT was optimized using cyclic voltammetry with respect to that of the Ag/AgCl reference electrode, and films were deposited from −0.6 V to −0.9 V at the working temperature of 75 °C. The as-prepared CIT films exhibited an amorphous nature, whereas the RTP-annealed films exhibited a highly crystalline chalcopyrite nature as a function of the growth potential. A red shift was observed in the Raman spectra of the as-deposited films that shifted towards the original position upon annealing. The Cu/In ratio obtained by the EDS analysis was found to decrease systematically upon increasing the growth potential. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) studies revealed the presence of Cu+, Cu2+ satellites, In3+, Te2−, and Te4+ states of Cu, In, and Te. The field emission study showed a maximum current density of 1.74 mA cm−2, which was attainable at an applied electric field of 1.5 V μm−1. The turn-on field was found to be 0.92 V μm−1, comparable to that of the carbon nanofibres. The emitter exhibited stable electron emission over a period of 3 hours. The faceted CIT nanorods with columnar growth are a potential candidate for application as an electron source, and herein, the field emission of CIT nanorods is reported for the first time.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...