Eco-friendly synthesis of SnSe nanoparticles: effect of reducing agents on the reactivity of a Se-precursor and phase formation of SnSe NPs†
Abstract
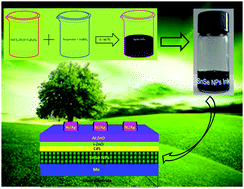
Tin monoselenide (SnSe) nanoparticles (NPs) have great potential to replace the conventional absorbers used in the fabrication of thin film solar cells. However, studies pertaining to the synthesis and fabrication of SnSe NPs-based solar cells are still lacking. This study presents an eco-friendly synthesis of SnSe NPs by a chemical precipitation method in a short reaction time of 10 min. The effect of different reducing agents (such as NaOH, ethylenediamine, Na2SO3, and NaBH4) on the reactivity of a Se-precursor and phase formation of SnSe NPs was investigated in detail. Our study indicated that the reaction between Sn2+ ions complexed by ascorbic acid and Se2− ions provided by the reduction with NaBH4 resulted in the formation of single phase SnSe NPs. For the first time, a SnSe NPs thin film inorganic solar cell with the device structure of SLG/Mo/SnSe NPs/CdS/i-ZnO/Al:ZnO/Ni/Ag was fabricated and tested, which showed an efficiency of 0.43%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...