Anticarcinogenic and metal chelation properties of novel hydroxybenzylidene-1-indanone derivatives in the U-251 glioblastoma cell line†
Abstract
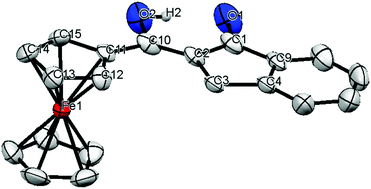
A novel series of (Z)-2-(hydroxy(aryl)methylene)-2,3-dihydro-1H-indanone derivatives were designed, synthesized and evaluated as cytotoxic agents against six cancer cell lines. In vitro studies showed that most of the molecules exhibited significant activity and selectivity towards the U-251 glioblastoma cell line, especially compounds 1 and 4, which were shown to have a lower IC50 value than that of temozolomide (TMZ) and promoted apoptosis in these cells. The compounds were also shown to be metal chelators, particularly iron chelators (Fe2+, Fe0 and Fe3+) that form iron(III) complexes, an important anticancer property. Compounds 8a and 1b, in particular, formed complexes with an IC50 value markedly lower than that of TMZ and showed pro-apoptotic activity. Basic structure–activity relationship analysis indicated that the skeleton base of 1-indanone and the aryl group are coplanar, and that the electron-donating methoxy moiety was responsible for the selective cytotoxic response.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...