A chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer for the determination of indolyl acetic acid using luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots as acceptors
Abstract
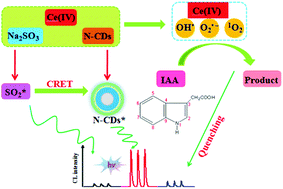
A chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer (CRET) method was fabricated for the determination of indolyl acetic acid (IAA) by using Ce(IV)–Na2SO3 in a chemiluminescence (CL) reaction as the donor and luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) as the acceptor. The CL intensity from the redox reaction of Ce(IV) and Na2SO3 in acidic medium increased significantly in the presence of N-CDs because the absorption band of N-CDs perfectly overlapped with the luminescence spectra of excited SO2 from the reaction of Ce(IV)–Na2SO3. Further, IAA was observed to inhibit the CL signal of the N-CDs–Ce(IV)–Na2SO3 system, which made it applicable for the determination of IAA. The linear range was 2.0 × 10−8–1.0 × 10−6 mol L−1 and the detection limit was 5.6 × 10−9 mol L−1. This work is not only of importance for gaining a better understanding of the unique optical and physical chemistry properties of doping carbon dots with heteroatoms but also has great potential to find CL applications in many fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...