Cu(i) complexes of dihydrobis(2-mercapto-benzimidazolyl)borate and dihydrobis(2-mercapto-benzothiazolyl)borate ligands: structural, photophysical and computational studies†
Abstract
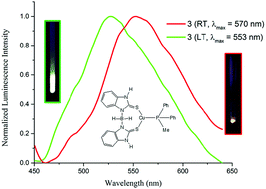
The salt metathesis reaction of CuI with two sodium precursors (NaBb and NaBb-1) of bipodal scorpionate type ligands [Bb = dihydrobis(2-mercapto-benzimidazolyl)borate, (Bb-1 = dihydrobis(2-mercapto-benzothiazolyl)borate)] has been explored in the presence of selected phosphine ligands (PPh3, PCy3, PPh2Me, PPh2Py). All of the resulting Cu(I) complexes were formed as predominantly a single monomeric isomer and were characterized using a combination of 1H, 13C{1H}, and 31P{1H} NMR spectroscopy, and in two cases by X-ray crystallography. In the X-ray crystal structure of complexes 1 and 6, the Cu(I) center adopts a distorted tetrahedral geometry. Complexes 1 and 6 exhibit (B)H⋯Cu distances of 2.008 Å and 1.866 Å length, respectively. Based on IR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography data, 1 and 6 adopt a κ3-S,S,H coordination mode in the solid state. All the metal complexes were screened for their photoluminescence properties in the solid state at different temperatures (298 K and 77 K). These complexes feature emission bands at room temperature in the range 527–571 nm, among which complex 3 and complex 6 reveal stronger thermochromic behavior at lower temperature. The data from the X-ray crystallography studies for 1 and 6 were used to optimize their structures computationally. Density Functional Theory (DFT) analyses were also conducted on the optimized structures to learn about the sources of electronic transitions in these complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...