La activated high surface area titania float for the adsorption of Pb(ii) from aqueous media
Abstract
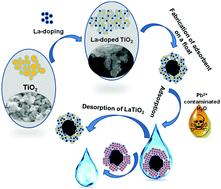
Currently, the world faces alarming challenges of heavy metal contamination, which are hazardous to humans and the environment because of their toxicity even in trace concentrations. Lead is one of the harmful heavy metal contaminants and has poisonous effects on human health. The present research investigation describes the adsorption of toxic Pb(II) on an immobilized adsorbent with a highly smaller crystallite size along with enhanced surface area and pore volume of La doped TiO2 synthesized from a simple co-precipitation method. Induction of dopant La3+ was confirmed by XPS with a smaller particle size of 25 nm as compared to TiO2 of 80 nm. The La doped TiO2 shows an enhanced surface area of 97.246 m2 g−1 compared to TiO2 of 17.2 m2 g−1 due to the introduction of oxygen vacancies leading to increased surface roughness and thus shows significant improvement in the adsorption of Pb(II) in comparison with TiO2 at basic pH due to the negative charge on La doped TiO2. A suitable optimized pH was examined and the Pb(II) adsorption study was measured using atomic absorption spectroscopy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...