Isolation and characterization of novel degradation products in cilnidipine by LC-QTOF-MS/MS, LCMSn, 2D-NMR and FTIR†
Abstract
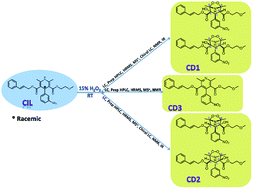
Cilnidipine (CIL) is a novel calcium antagonist accompanied with L-type and N-type calcium channel blocking functions. The drug was subjected to stress studies as per the international conference on harmonization guidelines (ICH) Q1A (R2) to understand the degradation profile of the drug. In the present study, seven degradation products were detected by simple mass compatible high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and tentatively characterized using high resolution mass spectrometry. Of these, three oxidative degradation (CD1, CD2 & CD3) products were isolated from the reaction mass using preparative HPLC and their structures were elucidated comprehensively using high resolution and multistage mass fragmentation studies, multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance and in spectroscopic techniques. Formation of racemic mixtures for each CD1 and CD2 were verified by chiral HPLC. Stereo centers for CD1 and CD2 were fixed using ROESY data as 1S, 2S, 3S, 4R, 5R (and its enantiomer) and 1S, 2S, 3R, 4R, 5R (and its enantiomer). To the best of our knowledge, CD1 and CD2 were novel structures which have not been discussed in any form of publication as yet. The proposed structures of CD1, CD2 and CD3 have been rationalized by appropriate mechanisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...