Omics approaches for subcellular translation studies
Abstract
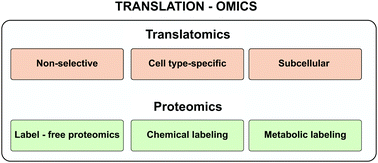
Compartmentalized translation allows rapid synthesis of proteins in targeted cellular locations. Microarray and RNA sequencing combined with physical subcellular separation methods have enabled extensive charting of subcellular transcriptomes. However, the extent of translating these local messages into protein remains relatively understudied at the genome-wide level. Here we review omics methods currently available for these studies, placing special attention on methods allowing cell-specific and subcellularly restricted analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...