Exciton photoluminescence and benign defect complex formation in zinc tin nitride†
Abstract
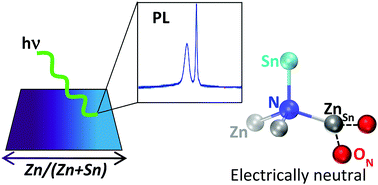
Emerging photovoltaic materials need to prove their viability by demonstrating excellent electronic properties. In ternary and multinary semiconductors, disorder and off-stoichiometry often cause defects that limit the potential for high-efficiency solar cells. Here we report on Zn-rich ZnSnN2 (Zn/(Zn + Sn) = 0.67) photoluminescence, high-resolution X-ray diffraction, and electronic structure calculations based on Monte-Carlo structural models. The mutual compensation of Zn excess and O incorporation affords a desirable reduction of the otherwise degenerate n-type doping, but also leads to a strongly off-stoichiometric and disordered atomic structure. It is therefore remarkable that we observe only near-edge photoluminescence from well-resolved excitons and shallow donors and acceptors. Based on first principles calculations, this result is explained by the mutual passivation of ZnSn and ON defects that renders both electronically benign. The calculated bandgaps range between 1.4 and 1.8 eV, depending on the degree of non-equilibrium disorder. The experimentally determined value of 1.5 eV in post-deposition annealed samples falls within this interval, indicating that further bandgap engineering by disorder control should be feasible via appropriate annealing protocols.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...