Copper(ii) complexes based on quinoline-derived Schiff-base ligands: synthesis, characterization, HSA/DNA binding ability, and anticancer activity†
Abstract
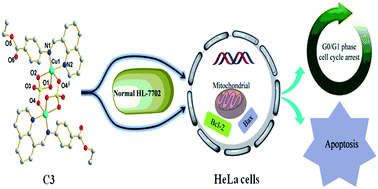
Three copper(II) complexes, [Cu(L1)(NO3)2] (C1), [Cu(L2)Cl2] (C2) and [Cu(L2)SO4]2·H2O (C3), were designed and synthesized by the reaction of Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, CuCl2·2H2O and CuSO4·5H2O with a quinoline-derived Schiff base ligand, L1 or L2, prepared by the condensation of quinoline-8-carbaldehyde with 4-aminobenzoic acid methyl ester or 4-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester (benzocaine). The efficient bindings of the C1–C3 complexes with human serum albumin (HSA) and calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) were analyzed by spectroscopy and molecular docking. These complexes could significantly quench the fluorescence of HSA through the static quenching process, and hydrophobic interactions with HSA through the sub-domain IIA and IIIA cavities. The complexes bind to DNA via the intercalative mode and they fit well into the curved contour of the DNA target in the minor groove region. Furthermore, the interaction abilities of the Cu(II) complexes with HSA/DNA were greater as compared to their corresponding ligands. Interestingly, C1–C3, particularly C3, exhibited more cytotoxicity toward HeLa cells compared to normal HL-7702 cells and three other tumor cell lines (Hep-G2, NCI-H460, and MGC80-3). Their cytotoxicity toward the HeLa cell lines was 1.9–3.5-fold more potent than cisplatin. Further studies indicated that these complexes arrested the cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase and promoted tumor cell apoptosis via a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated mitochondrial pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...