Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of m-amidophenol derivatives as a new class of antitubercular agents†
Abstract
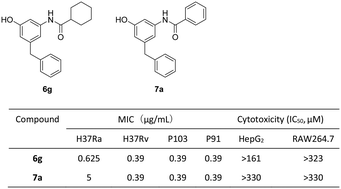
A series of m-amidophenol derivatives (6a–6l, 7a–7q, 9a, 9b, 12a–12c, 14 and 15) were designed and synthesized. Their antitubercular activities were evaluated in vitro against M. tuberculosis strains H37Ra and H37Rv and clinically isolated multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis strains. Ten compounds displayed minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) against M. tuberculosis H37Ra below 2.5 μg mL−1 and 6g was the most active compound (MIC = 0.625 μg mL−1). Compounds 6g and 7a also showed potent inhibitory activity against M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MIC = 0.39 μg mL−1) and several clinically isolated multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis strains (MIC = 0.39–3.125 μg mL−1). The compounds did not show inhibitory activity against normal Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. They exhibited low cytotoxicity against HepG2 and RAW264.7 cell lines. The results demonstrated m-amidophenol as an attractive scaffold for the development of new antitubercular agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...