Molecular modeling study, synthesis and biological evaluation of combretastatin A-4 analogues as anticancer agents and tubulin inhibitors†
Abstract
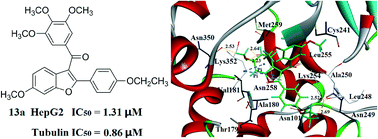
As the major structural component of microtubules, tubulin is an interesting target for the development of anticancer agents. In this study, 64 tubulin polymerization inhibitors of five-membered heterocycle-based combretastatin A-4 analogues were studied by a combination of molecular modeling techniques including 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. The CoMFA (comparative molecular field analysis) and CoMSIA (comparative molecular similarity indices analysis) models were established with desirable statistical parameters and excellent predictive ability. 20 ns MD simulations were successfully performed to confirm the detailed binding mode and validate the rationality of docking results. Combining the binding free energy calculations and 3D-QSAR results, some new heterocycle-based combretastatin A-4 analogues were designed. Three of them were synthesized and biologically evaluated. Compound 13a displayed potent antiproliferative activity (IC50 value of 1.31 μM against HepG2 cells, IC50 value of 1.37 μM against A549 cells) and inhibition of tubulin polymerization activity (IC50 value of 0.86 μM). Compound 13b also presented good activity against HepG2 cells (IC50 value of 4.75 μM). The experimental results demonstrated that the built models were effective for the development of novel anticancer agents and tubulin inhibitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...