Antimony speciation analysis by hydride trapping on hybrid nanoparticles packed in a needle trap device with electro-thermal atomic absorption spectrometry determination†
Abstract
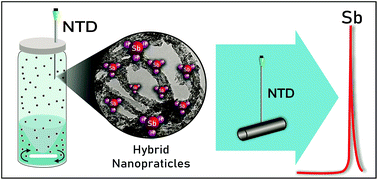
Oxidized multiwall carbon nanotubes (oxMWCNTs) were combined with TiO2 nanoparticles to obtain hybrid nanoparticles (HNPs). A miniaturized flow injection (FI) system was introduced for antimony speciation and a headspace vial was used for hydride generation. HNPs were introduced into a needle trap device (NTD) as a sorbent for antimony hydride preconcentration in gas phase trapping. Antimony hydrides were adsorbed on HNPs. Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (ETAAS) was used for determination. The synergistic effect of HNPs improves Sb adsorption compared to oxMWCNTs reaching the quantitative preconcentration of the analyte in 1 minute. However, NaBH4 concentration, HCl concentration and the elution volume were selected as variables for optimization. A Box–Behnken design indicated that the optimal response is achieved using 0.5% NaBH4 (m v−1), 1.5 mol L−1 HCl and 40 μL volume of elution. After optimization a retention efficiency of 99.8% was achieved with a preconcentration factor of 100. The limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) were 0.4 and 1.2 ng L−1. The relative standard deviation was 7.9% (n = 10). The time of analysis was 14 minutes. The developed technique was successfully applied to the analysis of river water samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...