A numerical inversion method for improving the spatial resolution of elemental imaging by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry
Abstract
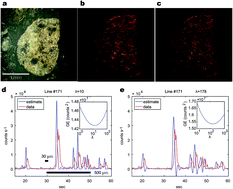
To improve the spatial resolution of the two-dimensional elemental images of solid organic and inorganic materials, a novel numerical correction method was developed for laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). Diffusion and dilution of LA aerosol particles in the carrier gas during transportation from the LA cell to the ICP are the major cause of image diffusion along the axis of a one-dimensional line scan. The correction calculations use (1) numerical forward modelling of the diffused elemental signals and (2) a non-negative signal deconvolution inversion calculation technique to retrieve the original signal profiles. This method improves spatial resolution with a semi-quantitative determination of the ablated masses. We used this method to sharpen the spatial distribution images of rhodium particles contained within a meteorite sample.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...