Covalent triazine framework catalytic oxidative cleavage of lignin models and organosolv lignin†
Abstract
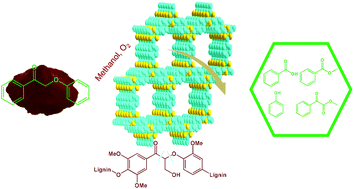
Covalent triazine frameworks (CTFs) were reported to be effective in the oxidative cleavage of the lignin model compound 2-phenoxyacetophenone, as metal-free catalysts with O2, producing phenol, benzoic acid, methyl benzoate and methyl benzoylformate as the major products. Combining the detailed characterizations with the reaction results, the triazine structure with unique properties of CTFs contributes to their superior catalytic performance. Mechanism investigation, including isotope-labeling, radical trapping and intermediate verification experiments, was carried out. CTFs promoted the decomposition of peroxide and cleavage of both the C–C bond and C–O bond occurred. The catalyst was reusable and very stable under the present reaction conditions. When CTFs were applied to the catalytic oxidative cleavage of organosolv lignin, nearly 80% of β-O-4 ketone bonds of the oxidized lignin were converted, suggesting the potential of CTFs in lignin depolymerization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...