d-Tagatose manufacture through bio-oxidation of galactitol derived from waste xylose mother liquor†
Abstract
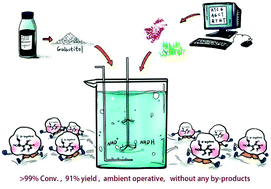
In this study, the bio-oxidation of galactitol to the valuable D-tagatose is presented. This proposed strategy could start with the refined by-product of waste xylose mother liquor formed by chemical hydrogenation. Through a computationally guided enzyme screening approach, a robust polyol dehydrogenase (PdPDH) was rapidly identified from a massive number of candidates. When coupled with a water-forming NADH oxidase (StNOX) for environmentally benign cofactor regeneration, subsequent reaction optimization facilitated the complete transformation of 100 g L−1 galactitol into the desired product within 15 h, with a yield of 91% in a 2 L scale preparative reaction. Compared to the current enzymatic isomerization system, our approach avoids low conversion, high operative temperatures and by-product formation, while enabling simplified product isolation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...