Efficient conversion of lignin into a water-soluble polymer by a chelator-mediated Fenton reaction: optimization of H2O2 use and performance as a dispersant†
Abstract
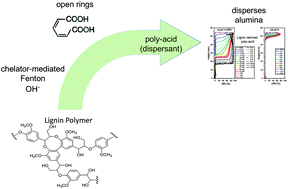
Room temperature Fenton (FEN) and chelator-mediated Fenton (CMF) reactions were examined for transforming lignin into a water-soluble polymer. Compared to depolymerization of lignin, this has the advantage of potentially yielding a product directly without requiring further upgrading. With the goal of optimizing the use of the expensive reagent H2O2, initial studies were performed with lignin from an organsolv process (OS) in thin films with a multi-well format that allows simultaneous assay of 76 reaction conditions. The results showed that H2O2 is more efficiently used in CMF compared with FEN, and that the greatest amount of lignin solubilized per mass of H2O2 consumed occurs at low initial concentrations of H2O2 (<1%). Further optimization of reaction conditions was performed with OS lignin in powder form. Results obtained upon optimizing reactant concentrations, pH and Fe-chelator, and with O2 bubbling indicate that a yield of 1 g lignin solubilized per g of H2O2 consumed is achievable. Chemical and molecular weight analyses showed that the reaction results in extensive opening of the aromatic rings and generation of acid groups, yielding a water-soluble polymer with molecular weight distribution that is comparable to that of the starting material but with a small amount of low MW species. Similar yields and extents of ring opening resulted for three other distinctly different lignins. The effectiveness of the OS lignin-derived polymeric material in dispersing alumina particles was studied by zeta potential, light scattering, and Turbiscan stability measurements. These measurements showed that the lignin-derived material performs comparably to poly(acrylic acid) PAA of similar molecular weight. Considering that the selling price for bulk PAA is greater than twice that of H2O2 on a per mass basis, this approach holds promise for generating value from lignin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...