Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of extracts from Chaenomeles sinensis (Thouin) Koehne in hyperuricemic mice
Abstract
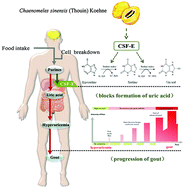
Clinically, Chaenomeles sinensis (Thouin) Koehne (C. sinensis) has been used to treat hyperuricemia and gout. However, the exact mechanism of action is still unknown. In the present study, the ethyl acetate fraction of C. sinensis fruit extract (CSF-E) was separated. Potassium oxonate (PO)-induced hyperuricemic mice and normal mice were administered with CSF-E at 60, 120 and 180 mg kg−1, respectively for 7 days. Serum uric acid, creatinine and BUN levels, liver oxidative damage, and serum and hepatic XOD activities were primarily measured using assay kits. The evaluation of its nephroprotective effects was carried out by renal histopathological analysis. Simultaneously, renal protein levels of organic anion transporters, such as mURAT1 and mOAT1, were detected using western blotting to elucidate the possible mechanisms. The results showed that CSF-E could significantly inhibit XOD activities in both serum and liver (p < 0.05), decreasing uric acid, creatinine and BUN levels in serum, and increasing levels in the excretion of uric acid by down-regulated of mURAT1 and up-regulated mOAT1 protein expression of kidney in hyperuricemic mice. Moreover, PO-induced alterations in the levels of MDA, hepatic SOD and GSH-Px activities and renal inflammation damage in hyperuricemic mice were effectively recovered by CSF-E at 120 mg kg−1. CSF-E possessed anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects by suppressing XOD activity, improving renal function and regulating renal mURAT1 and mOAT1 protein expression, which resulted in beneficial effects on hyperuricemia and gout prevention.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...