6-Gingerol as an arginase inhibitor prevents urethane-induced lung carcinogenesis by reprogramming tumor supporting M2 macrophages to M1 phenotype†
Abstract
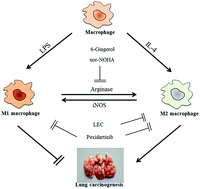
6-Gingerol (6-G) is the main bioactive component in Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). The aim of this study was to explore the contribution of macrophage polarization in 6-G-associated anti-cancer effects. In a urethane-induced lung carcinogenic model, lung carcinogenesis was positively correlated with macrophage (F4/80+) infiltration in lung interstitial in the control group. Furthermore, higher numbers of arginase+/F4/80+ M2 cells than iNOS+/F4/80+ M1 cells were observed in interstitial macrophages. Moreover, macrophage depletion by liposome-encapsulated clodronate (LEC) could significantly prevent lung carcinogenesis, whereas pexidartinib promoted lung carcinogenesis. After 6-G treatment, lung carcinogenesis was ameliorated with increased M1 macrophages and decreased M2 macrophages in the lung interstitial. ELISA showed that the levels of IFN-γ and IL-12 increased and the levels of IL-10 and TGF-β1 decreased in the alveolar cavity compared to those in the control group. Unexpectedly, the carcinogenesis-preventing efficacy of 6-G was promoted in LEC-treated mice, but completely aborted in pexidartinib-treated mice. In the in vitro experiment, 6-G reset the IL-4-induced arginase+ M2 cells toward iNOS+ M1 cells and exhibited reduced levels of arginase 1 and ROS and elevated levels of L-arginine and NO. LEC and nor-NOHA selectively suppressed M2 macrophages but had a negligible effect on M1 macrophages, whereas pexidartinib decreased both M2 and M1 macrophages. The iNOS+ macrophage-promoting efficacy of 6-G was increased by LEC, but was completely eliminated by pretreatment with pexidartinib or nor-NOHA. M2 macrophage-resetting efficacy of 6-G was confirmed in a Lewis lung cancer allograft model. This study indicated a reprogramming effect of 6-G as an arginase inhibitor on tumor supporting macrophages.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...