Polydatin protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic activities
Abstract
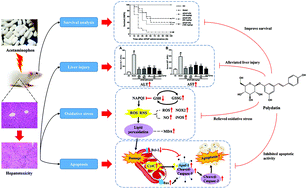
Acetaminophen (APAP) is commonly used to relieve pain and fever in a clinical setting, but its excessive use can lead to serious hepatotoxicity. Our previous study demonstrated that polydatin (PD) can effectively attenuate D-galactose- and alcohol-induced hepatotoxicity, however, its effect on APAP-induced hepatotoxicity is still unknown. In this study, we explore the protective effect and potential mechanism of PD against APAP-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. The results indicate that PD effectively improves the survival of mice with APAP-induced hepatotoxicity, significantly alleviating histopathologic alterations in the liver, and decreasing the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). PD significantly and dose-dependently reduces oxidative stress by lowering the content of oxidized glutathione (GSSG), reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitric oxide (NO) and malonaldehyde (MDA), while enhancing the hepatic activities of glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and the GSH/GSSG ratio. Meanwhile, PD also substantially inhibits the levels and mRNA expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2). Additionally, PD markedly arrests apoptosis by assuaging TUNEL-positive hepatocytes and the apoptotic index, decreasing the levels and expression of cytochrome c (CytC), cleaved-caspase-9, apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (Apaf-1), cleaved-caspase-3, and Bax and increasing the level and expression of Bcl-2. Overall, PD pretreatment shows a potent protective effect against APAP-induced hepatotoxicity by relieving oxidative stress and inhibiting apoptosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...