Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaf extract exerting anti-hyperglycemic activity by modulating GLUT4 and GLUT1 in the skeletal muscle of a diabetic mouse model
Abstract
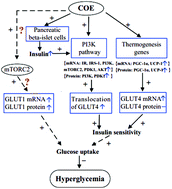
The present study aimed to explore the potent molecular mechanisms behind the hypoglycemic effect of Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaf extract (COE) in combination with a high-glucose-fat diet-fed and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse model. COE (50 and 200 mg per kg body weight per day) was given to the diabetic-model mice by intragastric administration for 4 weeks. It was found that the fasting blood glucose level (FBG), serum insulin level (FINS), and insulin sensitivity index (ISI) were significantly improved in the COE-treated diabetic-model mice. Glucose metabolism genes expression analysis of the skeletal muscle showed that COE exerted a glucose-lowering effect through the following two ways: on the one hand, COE enhanced insulin sensitivity by upregulating the transcription level of GLUT4, and in addition, it enhanced the insulin signaling pathway to promote the translocation of GLUT4 and upregulated thermogenesis genes expression, including PGC-1α and UCP-1; while on the other hand, GLUT1 expression was also increased in both the transcription and translation levels in the presence of COE. These two ways may result in promoting glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, thus leading to the reduction of the blood glucose level. The results suggested that COE ameliorated hyperglycemia in the diabetic-model mice through regulating glucose transporters, and then was likely to increase glucose uptake, which provided more evidence for applying COE to treat anti-hyperglycemia.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...