Increased intake of vitamin B12, folate, and omega-3 fatty acids to improve cognitive performance in offspring born to rats with induced hypertension during pregnancy
Abstract
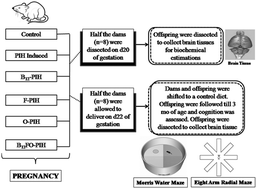
Vitamin B12, folic acid, and docosahexaenoic acid levels are reported to be altered in women with preeclampsia. This study examined the effect of the above nutrients on brain neurotrophins and on the cognitive performance in adult offspring in a pregnancy-induced hypertension rat model. Pregnant dams were assigned to control, PIH-induced, and PIH-induced supplemented with vitamin B12, folate, omega-3 fatty acids, and the combined supplementation of vitamin B12, folate, and omega-3 fatty acids groups. In the PIH group, brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels (BDNF) were lower in the offspring at birth, while the adult offspring showed lower levels of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in the hippocampus and BDNF (p < 0.05 for both) in the cortex as compared to in the control group. They also demonstrated higher (p < 0.05) escape latency in the Morris water maze test and performed a greater (p < 0.01 for all) number of errors in the Radial eight-arm maze test. A combined supplementation of vitamin B12, folic acid, and omega-3 fatty acids improved the levels of LCPUFA, neurotrophins, and cognition. A maternal diet consisting of high levels of folate, vitamin B12, and DHA reduced the risk for cognitive disorders in the adult offspring in an animal model of pregnancy-induced hypertension.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...