The chemical structure and anti-aging bioactivity of an acid polysaccharide obtained from rose buds
Abstract
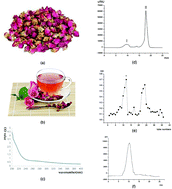
An acid polysaccharide, named R-PL, was extracted from rose buds by hot water (80 °C) extraction and purified by Sephadex G-200. R-PL, extracted with a total yield of 1.90%, is a highly pure polysaccharide with a total sugar content of 92.51%. A single and symmetrically sharp peak in its high-performance gel-permeation chromatography (HPGPC) spectrum indicates that R-PL is a homogeneous polysaccharide with a molecular weight of 7.727 × 105 Da. Monosaccharide composition analysis shows that it consists of D-arabinose, D-xylose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-galacturonic acid, and D-glucuronic acid with a molar ratio of 4.6 : 1.4 : 5.22 : 4.81 : 1 : 1.86. Structure analysis, such as FTIR spectroscopy, periodic acid oxidation, Smith degradation, methylation, and NMR analysis, reveals that R-PL has a backbone of →1)-α-D-Glcp-(6→ with side chains of →1)-β-D-Galp-(4,6→, →1)-β-D-Araf-(5→, →1)-α-D-Xylp-(4→, →1)-α-D-GlcpA-(2→ and →1)-α-D-GalpA-(4→. Its morphological characteristics were identified by Congo red experiments and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. The results show that R-PL does not have a triple-helical conformation in solution; its shape resembles twisted ribbons. Anti-oxidative and anti-aging analyses show that R-PL has significant antioxidant and anti-aging abilities in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...