Molecular actions of hypocholesterolaemic compounds from edible mushrooms
Abstract
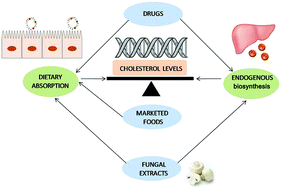
Cholesterol levels are strictly regulated to maintain its homeostasis; therefore, if it is not absorbed with the diet, the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway is enhanced and vice versa. Nowadays, the commonly prescribed therapeutic treatments for hypocholesterolemic patients are targeted toward the reduction of both cholesterol intestinal absorption and/or its endogenous biosynthesis. But, when hypercholesterolemia is still moderate the consumption of food products with cholesterol-lowering capacities is more desirable than using drugs. Marketed foods supplemented with hypocholesterolemic compounds are only inhibiting mechanisms for cholesterol absorption (i.e. phytosterols and cereal β-glucans). However, certain fungal extracts obtained from edible mushrooms might be able to modulate cholesterol levels by both strategies, pharmaceutical drugs and functional foods. In vitro and in vivo studies indicated that fungal sterols down-regulated genes involved in cholesterol homeostasis (such as Srebf2 and Nr1h4 (FXR)) and other specific mushroom extracts (β-glucans and other water-soluble compounds) also stimulated transcriptional profiles similar to simvastatin or ezetimibe (two hypocholesterolemic drugs). These and other observations suggested that the hypocholesterolemic effect of mushroom extracts could be due to transcriptional and post-transcriptional modulations besides other indirect effects.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Around the Supermarket: Staple Foods


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...