Spike sorting using non-volatile metal-oxide memristors†
Abstract
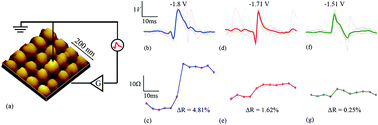
Electrophysiological techniques have improved substantially over the past years to the point that neuroprosthetics applications are becoming viable. This evolution has been fuelled by the advancement of implantable microelectrode technologies that have followed their own version of Moore’s scaling law. Similarly to electronics, however, excessive data-rates and strained power budgets require the development of more efficient computation paradigms for handling neural data in situ; in particular the computationally heavy task of events classification. Here, we demonstrate how the intrinsic analogue programmability of memristive devices can be exploited to perform spike-sorting on single devices. Leveraging the physical properties of nanoscale memristors allows us to demonstrate that these devices can capture enough information in neural signal for performing spike detection (shown previously) and spike sorting at no additional power cost.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New memory paradigms: memristive phenomena and neuromorphic applications

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...