Green synthesis of nanoscale anion exchange resin for sustainable water purification†
Abstract
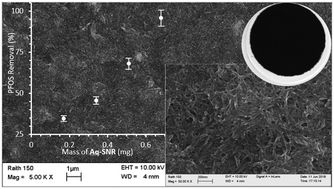
The challenge of providing safe and reliable drinking water is being exacerbated by accelerating population growth, climate change, and the increase of natural and anthropogenic contamination. Current water treatment plants are not effective at the removal of pervasive, hydrophilic, low molecular weight contaminants, which can adversely affect human health. Herein, we describe a green all-aqueous synthesis of an ion exchange resin comprised of short chain polyelectrolyte brushes covalently bound to single walled carbon nanotubes. This composite material is incorporated onto a membrane and the active sites are tested against analyte adsorption. Our control studies of water or brine pushed through these materials, found no evidence of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) or carbon/polymer coming out of the membrane filter. We have measured the adsorption capacity and percentage removal of ten different compounds (pharmaceuticals, pesticides, disinfection byproducts and perfluoroalkylated substances). We have measured their removal with an efficiency up to 95–100%. The synthesis, purification, kinetics, and characterization of the polyelectrolytes, and the subsequent nanoresin are presented below. The materials were tested as thin films. Regeneration capacity was measured up to 20 cycles and the material has been shown to be safe and reusable, enabling them as potential candidates for sustainable water purification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...