Rapid removal and recovery of emulsified oil from ASP produced water using in situ formed magnesium hydroxide†
Abstract
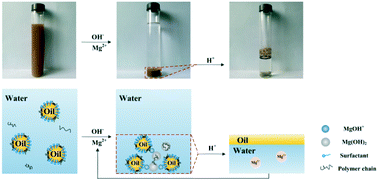
Due to the strong emulsion stability of alkaline/surfactant/polymer (ASP) produced water, its treatment and reuse constitute an urgent issue in the petroleum industry. This study presents an effective and economical method to decontaminate emulsified oil via in situ formed magnesium hydroxide (IFM). IFM was directly synthesized in ASP produced water by a wet precipitation method, which is simple for industrial production, and the emulsified oil was simultaneously removed during the precipitation process of IFM. The roles of contact time, pH, interface-active components, temperature, and initial oil concentration in oil removal were systematically investigated. Under optimal experimental conditions, the residue oil concentration could be reduced below 5.0 mg L−1 within 8 min. Even if the emulsion stability was enhanced by an increase in concentration of interface-active components, efficient oil removal could still be achieved. The adsorption capacity of IFM for oil was 10 959 mg g−1 at 293 K. MgOH+ played a significant role during treatment. The oil removal mechanism was mainly dominated by electrostatic attraction and the network structure of IFM. Crude oil could be recovered and the regenerated IFM maintained an oil removal efficiency of 91% in the fifth cycle. The results showed that the co-precipitation/adsorption process by IFM can be used as a promising technology for emulsified oil removal and recovery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...