Influence of spent filter backwash water recycling on pesticide removal in a conventional drinking water treatment process
Abstract
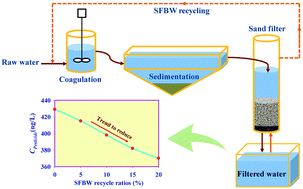
The effects of recycling spent filter backwash water (SFBW) on the removal of 14 organic pesticides were examined in a simulated conventional drinking water treatment process. The experimental results indicate that, the concentrations of these pesticides in the aqueous phase of SFBW remained unchanged although turbidity of the SFBW was increased greatly relative to the raw water during filter backwashing. With recycling of the SFBW, the concentration of pesticides in the blended influent raw water varied according to both the pesticide type and the recycling ratios. For the difficult to remove species, such as cyanazine and atrazine as well as carbaryl, even at high recycling ratios of SFBW the influent concentrations of the pesticides were almost the same. However, for those species that could be removed effectively, such as tolclofos-methyl, profenofos and chlorpyrifos, the influent concentrations decreased evidently with increasing recycling ratios. In addition, the mixing process of SFBW with raw water did not cause any noticeable pesticide release back into the solutions from the adsorbed surfaces of the clay particles in raw water or flocs in the SFBW. Moreover, the removal efficiencies of these pesticides under different recycling scenarios indicate that the SFBW recycling had no negative influence on pesticide removal. Finally, this study shows that, with SFBW recycling, the pesticide concentrations in filtered water were slightly lower than those without recycling and decreased considerably for hydrophobic pesticides as the recycling ratio increased.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...