Involvement of ethylene signaling in zinc oxide nanoparticle-mediated biochemical changes in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves†
Abstract
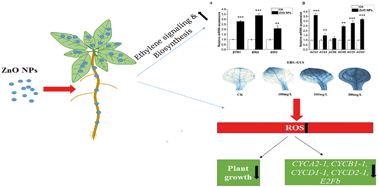
The growing use of metallic nanoparticles in industry has resulted in their accumulation in agricultural land, which poses a serious threat to the yield and quality of crops worldwide. Various reports showed that plants face environmental stress through hormones; however, the regulation of ethylene under ZnO NP stress is still unknown. In this study, ethylene-signaling defective mutants (etr1-3 and ein2-1) were studied in comparison to Arabidopsis wild-type under ZnO NPs stress. We found that ZnO NPs significantly inhibited the growth of Arabidopsis and induced toxicity by regulating the expression of cell cycle-related genes. More importantly our results showed the involvement of ethylene signaling and biosynthesis in this process. The ZnO NPs affected the biomass, and chlorophyll and sugar contents in both the ethylene-insensitive mutants and wild-type plants. The higher ROS accumulation and increased lipid peroxidation showed that the ZnO NPs induced toxicity in Arabidopsis. The observed high antioxidant enzyme activities and mRNA transcript levels of their corresponding genes in the mutant plants clearly showed the tolerance of the ethylene-insensitive mutants compared to the wild-type plant against oxidative damage caused by ZnO NP stress. Overall, our results showed that the ethylene-insensitive mutants tolerated ZnO NP-induced stress more efficiently than WT. These results suggest that ethylene induces oxidative damage in plants under ZnO NP stress.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...