Co-effects of UV/H2O2 and natural organic matter on the surface chemistry of cerium oxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
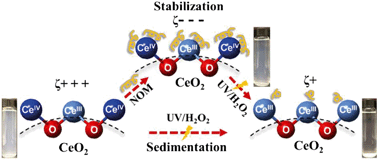
The widespread industrial applications of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles (NPs) have increased their likelihood of entering natural and engineered aqueous environments. This study investigates the surface chemistry changes of CeO2 NPs at pH 5.4 in the presence of both UV/H2O2 and natural organic matter (NOM). These conditions are relevant to advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). The results indicated that NOM stabilized CeO2 NPs in solution through surface complexation between the COO− functional groups of NOM and the CeO2 surfaces, reversing the zeta potential of CeO2 from 39.5 ± 2.7 mV to −38.3 ± 1.8 mV. UV/H2O2 treatment reduced the colloidal stability of CeO2 NPs, increased the percentage of Ce3+ on the surface from 17.8% to 28.3%, and lowered the zeta potential to close to neutral (3.8 ± 3.4 mV). With UV/H2O2 and NOM together, NOM coated on CeO2 NPs acted as a protective layer, making the direct reactions between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and CeO2 and their impacts on the colloidal stability insignificant in a short reaction period. During the UV/H2O2 treatment, the adsorption of superoxide radicals (O2˙−) dominated in neutralizing the surface charge of CeO2, leading to decreased electrostatic repulsive forces between nanoparticles and a higher extent of sedimentation. These new findings provide important implications for understanding the colloidal stability, sedimentation, and surface chemical properties of CeO2 NPs in aqueous systems where NOM and ROS are present.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...