Nitrate dynamics during impoundment and flood periods in a subtropical karst reservoir: Hongfeng Lake, Southwestern China
Abstract
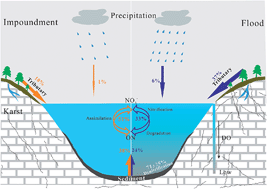
Nitrogenous species, particularly nitrate, are some of the most significant contaminants in freshwater rivers and lakes in China, posing a significant threat to human and ecosystem health. To identify the major nitrate sources and transformation processes in a subtropical karst lake (Hongfeng, HF) in Southwest China, two sampling campaigns involving three lake profiles were conducted during the impoundment period (April) and flood period (August). Hydro-chemistry parameters, concentration of nitrogenous species, and dual isotopes of nitrate were analyzed. Nitrate was the major nitrogenous species in HF lake with higher proportion in April than August. The concentrations of NH4+, NO2− and dissolved organic nitrogen were below the detection limit in April, while NH4+ increased with depth in August, which may be a result of mineralization. Nitrification was detected during the impoundment period and from the surface to a depth of 10 m during the flood period. Denitrification was detected in the lake bottom waters during the flood period with isotopic fractionation of −10.7‰ for δ15N–NO3− and −4.7‰ for δ18O–NO3−. The Rayleigh distillation demonstrated denitrification showed spatial variation (53% and 89% of nitrate in the southern and northern region of the lake, respectively). The Bayesian modelling results suggest that organic nitrogen degradation and sediment make the largest contributions to nitrate (51% and 38% in April and 33% and 24% in August, respectively) to the lake. Tributaries contributed more nitrate in August (37%) than in April (10%). The results highlight that modified endogenous nitrogen contributed a high proportion of nitrate sources within the lake system during the two periods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...