Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Taihu Lake, China: a review
Abstract
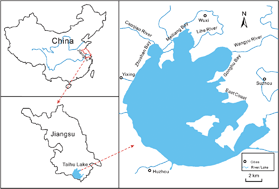
The rationale behind this paper was to review the available data regarding the current knowledge on the levels and trends of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Taihu Lake. The ecological risk associated with some of the PPCPs was also assessed. 36 PPCPs have been detected in the water, sediment and biota of Taihu Lake. These contaminants primarily emanate from anthropogenic activities in and around the lake. The northern part of the lake is highly polluted as compared to other parts because it receives most effluents from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), and domestic and industrial waste discharge from developed cities nearby. Based on the risk quotient (RQ) values, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, 17β-estradiol, roxithromycin and tetracycline may present a high ecological risk to organisms living in Taihu Lake. Regular monitoring is required to check the levels of PPCPs as they are regularly released into the lake. Investigations into the joint toxicities of PPCPs to aquatic organisms and the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and genes in Taihu Lake are highly recommended. Special attention in terms of policy and research should be given to the northern part of the lake.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...