Reduction of double manganese–cobalt oxides: in situ XRD and TPR study†
Abstract
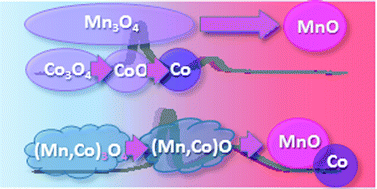
The work reported here was aimed at determining differences in redox properties of simple and double oxides. Comparison between the reduction of double oxides (Mn,Co)3O4 and simple oxides Co3O4 and Mn3O4 was performed using in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD), temperature-programmed reduction (TPR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The double oxides with a ratio of cations Mn : Co = 1 : 1 were prepared by the coprecipitation method and contained a mixture of 50% MnCo2O4 and 50% CoMn2O4. It was shown that the mechanism of reduction of double oxides with hydrogen differs significantly from the processes occurring on simple oxides. For simple cobalt and manganese oxides, transformations Co3O4 → CoO → Co and Mn3O4 → MnO are observed under a hydrogen atmosphere. The reduction of mixed-metal oxides occurs in two steps. In the first step, at 300–450 °C, (Mn,Co)3O4 transforms to (Mn,Co)O solid solutions. In situ XRD under isothermal conditions illustrates that Co-rich Co2MnO4 oxide starts to be reduced to Co0.6Mn0.4O first, and then Mn-rich Mn2CoO4 passes into Mn0.6Co0.4O. In the second step, at 450–700 °C, the reduction of solid solutions (Mn,Co)O to metallic cobalt Co and MnO proceeds. Again, the reduction begins with transformation of Co-rich oxide with the Co0.6Mn0.4O structure. The temperature of appearance of the intermediate phase (Mn,Co)O shifts to the higher values as compared to those observed for CoO, and to lower temperatures as compared to MnO during simple oxide reduction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...