Facile synthesis of metal nanoparticles decorated magnetic hierarchical carbon microtubes with polydopamine-derived carbon layer for catalytic applications†
Abstract
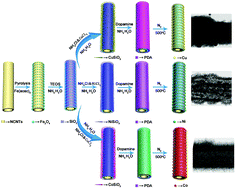
It is highly desirable but challenging to fabricate a unique hybrid material comprising nanosized copper/cobalt/nickel nanoparticles (NPs) uniformly distributed on magnetic supports. Herein in this work, hierarchical magnetic metal silicate hollow microtubes were prepared using silica coated magnetic N-doped carbon microtubes (NCMTs@Fe3O4@SiO2) as a chemical template; then polydopamine (PDA) was employed to coat onto magnetic metal silicate carbon microtubes (NCMTs@Fe3O4@CuSNTs/CoSNTs/NiSNTs), which can be carbonized to form hierarchical hybrid composites with uniformly-dispersed metallic copper/cobalt/nickel NPs embedded in PDA-derived carbon layers (NCMTs@Fe3O4@SiO2@C/Cu–Co–Ni). Owing to its hierarchical structure, large specific surface area as well as the high density of metal NPs, the resultant NCMTs@Fe3O4@SiO2@C/Ni–Co–Cu could be applied as catalysts towards the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). Furthermore, the NCMTs@Fe3O4@SiO2@C/Ni–Co–Cu catalysts could be easily collected and separated by applying an external magnetic field. In particular, it was found that NCMTs@Fe3O4@SiO2@C/Ni exhibited ultra-high catalytic activity on 4-NP reduction in comparison with Cu and Co supported catalysts. In addition, this unique hierarchical structure combined with magnetic recyclability make NCMTs@Fe3O4@SiO2@C/Ni a highly promising candidate for diverse applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...