Mechanistic insights into HCO2H dehydrogenation and CO2 hydrogenation catalyzed by Ir(Cp*) containing tetrahydroxy bipyrimidine ligand: the role of sodium and proton shuttle†
Abstract
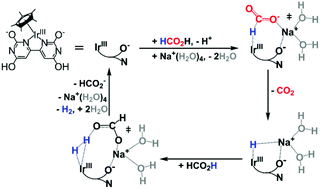
The mechanism of HCO2H dehydrogenation catalyzed by [IrCp*(H2O)(bpymO4H4)]2+ (bpymO4H4 = 2,2′,6,6′-tetrahydroxy-4,4′-bipyrimidine) was investigated using density functional theory. The relative free energy profiles at various protonation states corrected to pH 3.5 and pH 7.6 suggested that Na+ together with the ortho-oxyanion of bipyrimidine facilitates the Ir-HCO2 formation, subsequent hydride transfer, and H2 formation. HCO2H was found to be a more effective proton shuttle than H2O for H2 formation. Under experimental conditions, the highest catalytic reactivity was found at pH 3.5–4.0, where both HCO2Na and HCO2H were present. At lower pH and low formate concentration, HCO2H dehydrogenation tends to proceed via a Na+ independent pathway, involving a higher energy barrier. At higher pH, although Na+ can mediate hydride transfer and H2 formation, the low amount of HCO2H results in H2O as the proton shuttle, which involves a higher energy barrier than that for HCO2H proton shuttle. In other words, the catalytic activity of HCO2H dehydrogenation by the proton-responsive Ir complexes at different pH values is influenced by the protonation state, involvement of Na+, and the availability of HCO2H as a proton shuttle. For the hydrogenation of CO2 at pH 8.3, the rate determining step is the heterolytic cleavage of H2 mediated by Na+via a HCO3− proton shuttle. Our results demonstrate the importance of alkali metal ions in the design of catalysts for efficient, reversible, CO2 conversion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...