In situ intercalation of Au nanoparticles and magnetic γ-Fe2O3 in the walls of MCM-41 with abundant void defects for highly efficient reduction of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes†
Abstract
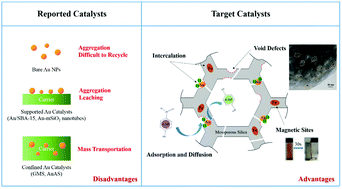
Nowadays, agglomeration and leaching of metal active sites during reaction and recycle processes are considered to be a thorny problem for noble metal-based catalysts. Therefore, to make improvements, nano-gold was selected as a representative research object for many noble metals. In this study, Au nanoparticles (NPs) and magnetic γ-Fe2O3 were intercalated in situ in the walls of MCM-41 via a one-pot hydrothermal method, in which the intercalation process was preceded by co-condensation of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) with MPTS-Au complexes ((3-mercaptopropyl)-trimethoxysilane (MPTS), HAuCl4·3H2O), and a Fe3O4 sol. By the confinement of silica, Au NPs and γ-Fe2O3 were well dispersed in the walls of MCM-41, the sintering and loss of Au NPs was highly restricted, and the magnetic property of γ-Fe2O3 facilitated the recycling of Au-based catalysts. Additionally, abundant void defects appeared in MCM-41 by assembly of micelles in different sizes and shapes, greatly improving the surface area of target catalysts (>1800 m2 g−1), which provided more opportunities for contact and collision between reactors and gold active sites, effectively solving the problem of mass transportation. As expected, a series FeAu@MCM-41 catalysts showed superior catalytic activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) and organic dyes (MB, RhB, and MO), and these catalysts were recycled five times without significant loss of metal species or catalytic activity. This is attributed to the confinement effect of the silica walls and the excellent magnetic properties of γ-Fe2O3. This special structure of FeAu@MCM-41 catalysts provides more insights for designing and fabricating noble metal-based catalysts with desirable performances.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...