Formation of uniform magnetic C@CoNi alloy hollow hybrid composites with excellent performance for catalysis and protein adsorption†
Abstract
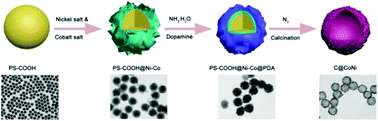
Metallic nickel- or cobalt-based composites with hollow nanostructures such as nanocages can serve as both advanced catalysts and protein adsorbents owing to their high surface area and increased active sites; hence, they have aroused great interest. Herein, we report a facile route to synthesize hollow carbon spheres (HCS) embedded with bimetallic NiCo nanoparticles (NPs) with hollow structures by using NiCo hydroxide layered nanosheet functionalized carboxyl polystyrene spheres (CPS) as a template and polydopamine (PDA) as both the carbon precursor and reductant. This unique hierarchical architecture, including meso- and macro-pores, provides a large specific surface area (244 m2 g−1) and efficient channels for the diffusion of small molecules and biomacromolecules (protein). These features greatly facilitate the excellent performances of C@CoNi for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and His-rich protein adsorption. Moreover, the size of the surficial CoNi NPs can be facilely modulated by changing the calcination temperature, which can effectively control the catalytic and adsorption performances of the as-prepared nanocomposites. The as-prepared C@CoNi is employed as a catalyst to investigate its catalytic performance in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). Furthermore, the nickel nanoparticles decorated on the hollow microspheres display a strong affinity to His-rich proteins (BHb and BSA) via specific metal affinity forces between the polyhistidine groups and nickel nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...