Towards the rational design of the Py5-ligand framework for ruthenium-based water oxidation catalysts†
Abstract
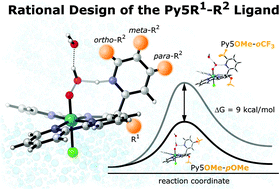
In order to rationally design water oxidation catalysts (WOCs), an in–depth understanding of the reaction mechanism is essential. In this study we showcase the complexity of catalytic water oxidation, by elucidating how modifications of the pentapyridyl (Py5) ligand-framework influence the thermodynamics and kinetics of the process. In the reaction mechanism the pyridine–water exchange was identified as a key reaction which appears to determine the reactivity of the Py5–WOCs. Exploring the capabilities of in silico design we show which modifications of the ligand framework appear promising when attempting to improve the catalytic performance of WOCs derived from Py5.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent: Europe


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...