Cyclometalated iridium(iii) complexes induce mitochondria-derived paraptotic cell death and inhibit tumor growth in vivo†
Abstract
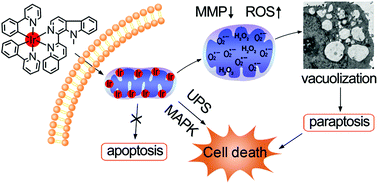
The development of iridium complexes as potent anticancer agents has received increasing attention in recent years. In this study, four cyclometalated Ir(III) complexes with good photophysical properties and potent anticancer activity have been synthesized and characterized. They are taken up by human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells very quickly and specifically target mitochondria. Mechanism studies reveal that one of them, namely IrM2, induces paraptosis accompanied by excessive mitochondria-derived cytoplasmic vacuoles. Meanwhile, IrM2 affects the ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. Furthermore, IrM2 rapidly induces a series of mitochondria-related dysfunctional events, including the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, cellular ATP depletion, mitochondrial respiration inhibition and reactive oxygen species (ROS) elevation. The rapid loss of mitochondrial functions, elevation of ROS and impairment of the UPS induced by IrM2 lead to the collapse of mitochondria and the subsequent cytoplasmic vacuolation before the cells are ready to start the mechanisms of apoptosis and/or autophagy. Among the ROS, superoxide anion radicals play a critical role in IrM2-mediated cell death. In vivo studies reveal that IrM2 can significantly inhibit tumor growth in a mouse model. This work gives useful insights into the design and anticancer mechanisms of new metal-based anticancer agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...