Flexibility of components alters the self-assembly pathway of Pd2L4 coordination cages†
Abstract
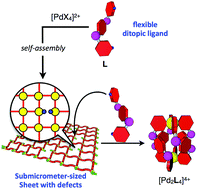
The self-assembly process of a Pd2L4 cage consisting of flexible ditopic ligands and Pd(II) ions was revealed by QASAP (quantitative analysis of self-assembly process), which enables one to obtain information about the intermediates transiently produced during the self-assembly as the average composition of all the intermediates. It was found that the dominant pathway to the cage is the formation of a submicrometre-sized sheet structure, which was characterized by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM), followed by the addition of free ditopic ligands to the Pd(II) centres of the sheet structure to trigger the cage formation. This assembly process is completely different from that of a Pd2L4 cage composed of rigid ditopic ligands, indicating that the flexibility of the components strongly affects the self-assembly process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...