A theoretical study on the mechanism of hydrogenation of carboxylic acids catalyzed by the Saito catalyst†
Abstract
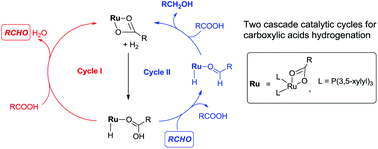
The mechanism of the ruthenium carboxylate-catalyzed hydrogenation of carboxylic acids was investigated by using density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The novel mechanism including two hydrogenation cycles was proposed for this reaction. The first cycle is the hydrogenation of the carboxylic acid to an aldehyde, while the second cycle is the hydrogenation of the aldehyde to an alcohol. These two catalytic cycles share similar elementary steps, including H2 heterolysis, hydride migration of the carboxylic acid or aldehyde, and catalyst regeneration. In this hydrogenation mechanism, the carboxylic acid is not only a reactant, but also an important proton source. Furthermore, the noncovalent interaction (e.g. hydrogen bonding interaction) between the ligand and carboxylic acid substrate could promote the hydrogenation of the carboxylic acid through stabilizing the transition state of the most energy-demanding step (i.e., hydride migration in the first catalytic cycle). Besides, the strong electron-donating ability of the dppb ligand could also facilitate the hydride migration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...