Two-step electrodeposition to fabricate the p–n heterojunction of a Cu2O/BiVO4 photoanode for the enhancement of photoelectrochemical water splitting
Abstract
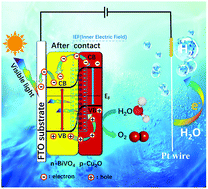
A Cu2O/BiVO4 p–n heterojunction based photoanode in photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is fabricated by a two-step electrodeposition method on an FTO substrate followed by annealing treatment. The structures and properties of the samples are characterized by XRD, FESEM, HRTEM, XPS and UV-visible spectra. The photoelectrochemical activity of the photoanode in water oxidation has been investigated and measured in a three electrode quartz cell system; the obtained maximum photocurrent density of 1.72 mA cm−2 at 1.23 V vs. RHE is 4.5 times higher than that of pristine BiVO4 thin films (∼0.38 mA cm−2). The heterojunction based photoanode also exhibits a tremendous cathodic shift of the onset potential (∼420 mV) and enhancement in the IPCE value by more than 4-fold. The enhanced photoelectrochemical properties of the Cu2O/BiVO4 photoelectrode are attributed to the efficient separation of the photoexcited electron–hole pairs caused by the inner electronic field (IEF) of the p–n heterojunction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...