Catalytic properties of pristine and defect-engineered Zr-MOF-808 metal organic frameworks†
Abstract
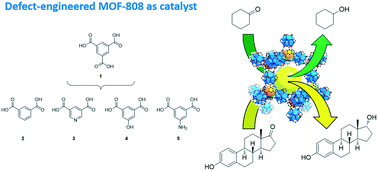
Various defect-engineered Zr-trimesate MOF-808 compounds (DE-MOF-808) have been prepared by mixing the tricarboxylate ligands with dicarboxylate ligands; viz. isophthalate, pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, 5-hydroxy-isophthalate, or 5-amino-isophthalate. The resulting mixed-ligand compounds, MOF-808-X (X = IP, Pydc, OH or NH2) were all found to be highly crystalline and isostructural to the unmodified MOF-808. Pristine MOF-808 showed better catalytic performance than a UiO-66 reference compound for the Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley (MPV) reduction of carbonyl compounds. This was attributed to a higher availability of coordinatively unsaturated Zr4+ sites (cus) in MOF-808 upon removal of formate ions. Meanwhile, cus in UiO-66 are only located at defect sites and are thus much less abundant. Further improvement of the catalytic activity of defect-engineered MOF-808-IP and MOF-808-Pydc was observed, which may be related with the occurrence of less crowded Zr4+ sites in DE-MOF-808. The wider pore structure of MOF-808 with respect to UiO-66 compounds translates into a sharp improvement of the activity for the MPV reduction of bulky substrates, as shown for estrone reduction to estradiol. Interestingly, MOF-808 produces a notable diastereoselectivity towards the elusive 17-α-hydroxy estradiol.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...