Dihydroxyacetone conversion into lactic acid in an aqueous medium in the presence of metal salts: influence of the ionic thermodynamic equilibrium on the reaction performance†
Abstract
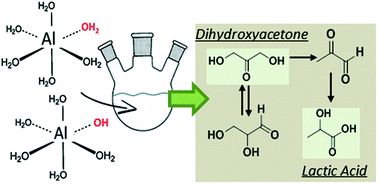
The catalytic conversion of dihydroxyacetone (DHA) to lactic acid (LA) via pyruvaldehyde (PA) in an aqueous medium was studied using different homogeneous metal salts. A kinetic model was developed and the parameters corresponding to each reaction step were estimated. Agreement between experiments and simulated results was excellent and the performance of the different catalysts was consistent with previous studies described in the literature. Aluminium salts, which show the best performance, were tested in a whole range of concentrations and at different pH values in order to identify the catalytically active ionic species. It was confirmed that the DHA to pyruvaldehyde (PA) dehydration step is catalyzed by both Brønsted and Lewis acids, whereas the consecutive reaction of PA to LA is catalyzed solely by Lewis acids. Moreover, a comparison of the thermodynamic analysis of the reaction medium and the kinetic parameters demonstrated that cationic hydroxyl-aluminium complexes [Al(OH)h](3−h)+ formed in situ by the hydrolysis of aluminium aqua complexes like [Al(OH2)6]3+ are the most active Lewis acids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...