Silver cyanamide nanoparticles decorated ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalysis†
Abstract
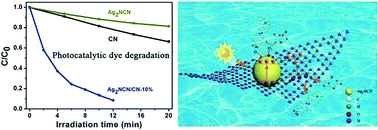
Metal cyanamide compounds are an emerging class of photoactive materials for solar energy applications. Although silver cyanamide (Ag2NCN) applied in visible-light-driven photocatalysis has been demonstrated, the photocatalytic performance is unsatisfactory. Herein, a composite of Ag2NCN nanoparticles supported on ultrathin carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets is synthesized by combining thermal annealing and an in situ precipitation method. Due to the band alignment between Ag2NCN and g-C3N4, a type-II semiconductor heterojunction is built up to improve the photocatalytic activity of pristine Ag2NCN. The as-prepared nanocomposites exhibit enhanced photocatalytic activity for organic dye decolorization under visible light irradiation compared with pure Ag2NCN and pristine g-C3N4 nanosheets. The enhancement of photocatalytic performance can be ascribed to the synergistic effects between Ag2NCN and g-C3N4, which include improved light absorption, superior charge separation, uniform dispersion and smaller size of Ag2NCN loaded on high surface area g-C3N4 nanosheets. The kinetics model and degradation mechanism of the nanocomposites are also proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...