Quantification of hyperpolarisation efficiency in SABRE and SABRE-Relay enhanced NMR spectroscopy†
Abstract
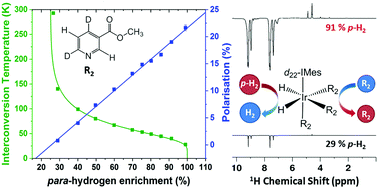
para-Hydrogen (p-H2) induced polarisation (PHIP) is an increasingly popular method for sensitivity enhancement in NMR spectroscopy. Its growing popularity is due in part to the introduction of the signal amplification by reversible exchange (SABRE) method that generates renewable hyperpolarisation in target analytes in seconds. A key benefit of PHIP and SABRE is that p-H2 can be relatively easily and cheaply produced, with costs increasing with the desired level of p-H2 purity. In this work, the efficiency of the SABRE polarisation transfer is explored by measuring the level of analyte hyperpolarisation as a function of the level of p-H2 enrichment. A linear relationship was found between p-H2 enrichment and analyte 1H hyperpolarisation for a range of molecules, polarisation transfer catalysts, NMR detection fields and for both the SABRE and SABRE-Relay transfer mechanisms over the range 29–99% p-H2 purity. The gradient of these linear relationships were related to a simple theoretical model to define an overall efficiency parameter, E, that quantifies the net fraction of the available p-H2 polarisation that is transferred to the target analyte. We find that the efficiency of SABRE is independent of the NMR detection field and exceeds E = 20% for methyl-4,6-d2-nicotinate when using a previously optimised catalyst system. For the SABRE-Relay transfer mechanism, efficiencies of up to E = 1% were found for 1H polarisation of 1-propanol, when ammonia was used as the polarisation carrier.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...